算法-最短路径

最短路径
Dijkstra 算法
基于贪心的单源最短路算法,其要求图中的边全部非负。
算法描述
procedure Dijkstra(G:边全为正权的图) 2 {G带有顶点 $a=v_{0},v_{1},v_{2}…$}和若干边 $w(v_{i},v_{j})$ 3 for i:=1 to n 4 $D(v_{i}):=\infty $ 5 D(a):=0 6 $S:=\emptyset$ 7 while $z\notin S$ 8 begin 9 u:=不属于S的D(u)最小的一个顶点 10 $S:=S\cup {u}$ 11 for 所有不属于S的顶点v 12 if D(u)+w(u,v)<D(v) then D(v):=D(u)+w(u,v) 13 end{D(z)=从a到z的最短路长度}
使用优先队列
1 function Dijkstra(G, w, s) 2 INITIALIZE-SINGLE-SOURCE(G, s) //实际上的操作是将每个除原点外的顶点的d[v]置为无穷大,d[s]=0 3 $S\leftarrow \emptyset$ 4 $Q\leftarrow s$ // Q是顶点V的一个优先队列,以顶点的最短路径估计排序 5 while( $Q\not =\emptyset $) 6 do $u\leftarrow EXTRACT-MIN(Q)$ //选取u为Q中最短路径估计最小的顶点 7 $S\leftarrow S\cup u$ 8 for each vertex $v \in Adj[u]$ 9 do RELAX(u, v, w) //松弛成功的结点会被加入到队列中
http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/16221 :
Pseudo code :
dijkstra(v) :
d[i] = inf for each vertex i
d[v] = 0
s = new empty set
while s.size() < n
x = inf
u = -1
for each i in V-s //V is the set of vertices
if x >= d[i]
then x = d[i], u = i
insert u into s
// The process from now is called Relaxing
for each i in adj[u]
d[i] = min(d[i], d[u] + w(u,i))
int mark[MAXN];
void dijkstra(int v){
fill(d,d + n, inf);
fill(mark, mark + n, false);
d[v] = 0;
int u;
while(true){
int x = inf;
u = -1;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++)
if(!mark[i] and x >= d[i])
x = d[i], u = i;
if(u == -1) break;
mark[u] = true;
for(auto p : adj[u]) //adj[v][i] = pair(vertex, weight)
if(d[p.first] > d[u] + p.second)
d[p.first] = d[u] + p.second;
}
}
Two) 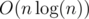
- Using
std :: set:
void dijkstra(int v){
fill(d,d + n, inf);
d[v] = 0;
int u;
set<pair<int,int> > s;
s.insert({d[v], v});
while(!s.empty()){
u = s.begin() -> second;
s.erase(s.begin());
for(auto p : adj[u]) //adj[v][i] = pair(vertex, weight)
if(d[p.first] > d[u] + p.second){
s.erase({d[p.first], p.first});
d[p.first] = d[u] + p.second;
s.insert({d[p.first], p.first});
}
}
}
- Using
std :: priority_queue(better):
bool mark[MAXN];
void dijkstra(int v){
fill(d,d + n, inf);
fill(mark, mark + n, false);
d[v] = 0;
int u;
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int> >, greater<pair<int,int> > > pq;
pq.push({d[v], v});
while(!pq.empty()){
u = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if(mark[u])
continue;
mark[u] = true;
for(auto p : adj[u]) //adj[v][i] = pair(vertex, weight)
if(d[p.first] > d[u] + p.second){
d[p.first] = d[u] + p.second;
pq.push({d[p.first], p.first});
}
}
}
Problem: ShortestPath Query
Implement 1
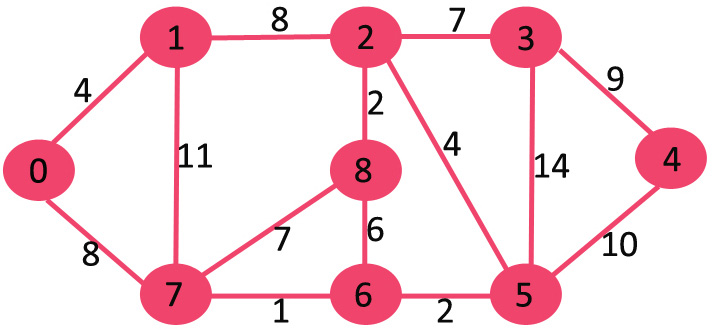
// A C++ program for Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm.
// The program is for adjacency matrix representation of the graph
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <limits.h>
// Number of vertices in the graph
#define V 9
// A utility function to find the vertex with minimum distance value, from
// the set of vertices not yet included in shortest path tree
int minDistance(int dist[], bool sptSet[])
{
// Initialize min value
int min = INT_MAX, min_index;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (sptSet[v] == false && dist[v] <= min)
min = dist[v], min_index = v;
return min_index;
}
// A utility function to print the constructed distance array
void printSolution(int dist[])
{
cout <<"Vertex \t Distance from Source" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
cout << i << " \t\t"<<dist[i]<< endl;
}
// Function that implements Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm
// for a graph represented using adjacency matrix representation
void dijkstra(int graph[V][V], int src)
{
int dist[V]; // The output array. dist[i] will hold the shortest
// distance from src to i
bool sptSet[V]; // sptSet[i] will be true if vertex i is included in shortest
// path tree or shortest distance from src to i is finalized
// Initialize all distances as INFINITE and stpSet[] as false
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dist[i] = INT_MAX, sptSet[i] = false;
// Distance of source vertex from itself is always 0
dist[src] = 0;
// Find shortest path for all vertices
for (int count = 0; count < V - 1; count++) {
// Pick the minimum distance vertex from the set of vertices not
// yet processed. u is always equal to src in the first iteration.
int u = minDistance(dist, sptSet);
// Mark the picked vertex as processed
sptSet[u] = true;
// Update dist value of the adjacent vertices of the picked vertex.
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
// Update dist[v] only if is not in sptSet, there is an edge from
// u to v, and total weight of path from src to v through u is
// smaller than current value of dist[v]
if (!sptSet[v] && graph[u][v] && dist[u] != INT_MAX
&& dist[u] + graph[u][v] < dist[v])
dist[v] = dist[u] + graph[u][v];
}
// print the constructed distance array
printSolution(dist);
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Let us create the example graph discussed above */
int graph[V][V] = { { 0, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0 },
{ 4, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0 },
{ 0, 8, 0, 7, 0, 4, 0, 0, 2 },
{ 0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 14, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 9, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 4, 14, 10, 0, 2, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 1, 6 },
{ 8, 11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 7 },
{ 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 0 } };
dijkstra(graph, 0);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Implement 2: priority_queue
priority_queue 模板有 3 个参数,其中两个有默认的参数;第一个参数是存储对象的类型,第二个参数是存储元素的底层容器,第三个参数是函数对象,它定义了一个用来决定元素顺序的断言。因此模板类型是:
template <typename T, typename Container=std::vector<T>, typename Compare=std::less<T>> class priority_queue
如你所见,priority_queue 实例默认有一个 vector 容器。函数对象类型 less 是一个默认的排序断言,定义在头文件 function 中,决定了容器中最大的元素会排在队列前面。fonction 中定义了 greater,用来作为模板的最后一个参数对元素排序,最小元素会排在队列前面。当然,如果指定模板的最巵一个参数,就必须提供另外的两个模板类型参数。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
# define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
// iPair ==> Integer Pair(整数对)
typedef pair<int, int> iPair;
// 加边
void addEdge(vector <pair<int, int> > adj[], int u,
int v, int wt)
{
adj[u].push_back(make_pair(v, wt));
adj[v].push_back(make_pair(u, wt));
}
// 计算最短路
void shortestPath(vector<pair<int,int> > adj[], int V, int src)
{
// 关于stl中的优先队列如何实现,参考下方网址:
// http://geeksquiz.com/implement-min-heap-using-stl/
priority_queue< iPair, vector <iPair> , greater<iPair> > pq;
// 距离置为正无穷大
vector<int> dist(V, INF);
vector<bool> visited(V, false);
// 插入源点,距离为0
pq.push(make_pair(0, src));
dist[src] = 0;
/* 循环直到优先队列为空 */
while (!pq.empty())
{
// 每次从优先队列中取出顶点事实上是这一轮最短路径权值确定的点
int u = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if (visited[u]) {
continue;
}
visited[u] = true;
// 遍历所有边
for (auto x : adj[u])
{
// 得到顶点边号以及边权
int v = x.first;
int weight = x.second;
//可以松弛
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight)
{
// 松弛
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pq.push(make_pair(dist[v], v));
}
}
}
// 打印最短路
printf("Vertex Distance from Source\n");
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d \t\t %d\n", i, dist[i]);
}
int main()
{
int V = 9;
vector<iPair > adj[V];
addEdge(adj, 0, 1, 4);
addEdge(adj, 0, 7, 8);
addEdge(adj, 1, 2, 8);
addEdge(adj, 1, 7, 11);
addEdge(adj, 2, 3, 7);
addEdge(adj, 2, 8, 2);
addEdge(adj, 2, 5, 4);
addEdge(adj, 3, 4, 9);
addEdge(adj, 3, 5, 14);
addEdge(adj, 4, 5, 10);
addEdge(adj, 5, 6, 2);
addEdge(adj, 6, 7, 1);
addEdge(adj, 6, 8, 6);
addEdge(adj, 7, 8, 7);
shortestPath(adj, V, 0);
return 0;
}
P4779 单源最短路径
给定一个 n 个点,m 条有向边的带非负权图,请你计算从 s 出发,到每个点的距离。
数据保证你能从 s 出发到任意点。
Floyd
是一种基于动态规划的多源最短路算法
Floyd-Warshal()
d[v][u] = inf for each pair (v,u)
d[v][v] = 0 for each vertex v
for k = 1 to n
for i = 1 to n
for j = 1 to n
d[i][j] = min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j])
Time complexity : O(n3).
Bellman-Ford
不仅可以处理负权边,还能处理负环
对所有的点进行V-1次松弛操作,理论上就找到了从源点到其他所有点的最短路径.
如果还可以继续松弛, 说明原图中有环.
其优于迪科斯彻算法的方面是边的权值可以为负数、实现简单,缺点是时间复杂度过高,高达O(|V||E|)
贝尔曼-福特算法简单地对所有边进行松弛操作,共|V|-1次,其中|V|是图的点的数量
procedure BellmanFord(list vertices, list edges, vertex source)
// 讀入邊和節點的列表並對distance和predecessor寫入最短路徑
// 初始化圖
for each vertex v in vertices:
if v is source then distance[v] := 0
else distance[v] := infinity
predecessor[v] := null
// 對每一條邊重複操作
for i from 1 to size(vertices)-1:
for each edge (u, v) with weight w in edges:
if distance[u] + w < distance[v]:
distance[v] := distance[u] + w
predecessor[v] := u
// 檢查是否有負權重的回路
for each edge (u, v) with weight w in edges:
if distance[u] + w < distance[v]:
error "圖包含負權重的回路"
http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/16221 :
Bellman-Ford(int v)
d[i] = inf for each vertex i
d[v] = 0
for step = 1 to n
for all edges like e
i = e.first // first end
j = e.second // second end
w = e.weight
if d[j] > d[i] + w
if step == n
then return "Negative cycle found"
d[j] = d[i] + w
Time complexity : O(nm).
SPFA (Shortest Path Faster Algorithm)
国际上一般认为是队列优化的Bellman-Ford 算法
这里的


procedure Shortest-Path-Faster-Algorithm(G, s)
for each vertex v ≠ s in V(G)
d(v) := ∞
d(s) := 0
offer s into Q
while Q is not empty
u := poll Q
for each edge (u, v) in E(G)
if d(u) + w(u, v) < d(v) then
d(v) := d(u) + w(u, v)
if v is not in Q then
offer v into Q
http://codeforces.com/blog/entry/16221 :
SPFA(v):
d[i] = inf for each vertex i
d[v] = 0
queue q
q.push(v)
while q is not empty
u = q.front()
q.pop()
for each i in adj[u]
if d[i] > d[u] + w(u,i)
then d[i] = d[u] + w(u,i)
if i is not in q
then q.push(i)
References
Archives
2019/03 (14) 2020/08 (1) 2021/01 (2) 2021/05 (2) 2021/12 (2) 2022/03 (2) 2022/04 (2) 2023/12 (2) 2024/01 (5) 2024/04 (1) 2024/05 (1)Tags
Recent Posts